Cannabidiol, commonly known as CBD, has gained significant popularity in recent years due to its potential therapeutic benefits. However, to truly understand how CBD works and interacts with our bodies, it is essential to explore the endocannabinoid system.
The Endocannabinoid System
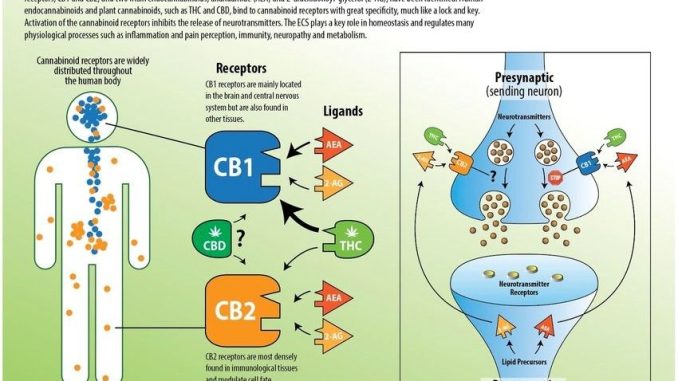
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex network of receptors and compounds that play a crucial role in maintaining balance and homeostasis within our bodies. It consists of three main components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes.
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds produced by our bodies. The two primary endocannabinoids identified so far are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). They are synthesized on-demand and act as neurotransmitters, transmitting signals within the ECS.
Receptors
There are two main types of receptors in the ECS – CB1 and CB2 receptors.
CB1 receptors: These are primarily found in the central nervous system, but they are also present in other parts of the body, such as the lungs, liver, and kidneys.
CB2 receptors: These receptors are mostly located in the immune system and peripheral tissues.
Enzymes
Enzymes are responsible for the synthesis and breakdown of endocannabinoids. The two main enzymes involved in this process are fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL).
How CBD Interacts with the ECS
CBD has a unique interaction with the endocannabinoid system. Unlike tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which binds directly to CB1 and CB2 receptors, CBD indirectly influences their activity.
Modulating Receptor Activity
CBD can modulate CB1 and CB2 receptors, enhancing or inhibiting their ability to bind with endocannabinoids. This modulation can impact various physiological processes, such as pain sensation, appetite, mood, and immune response.
Inhibiting Enzyme Activity
CBD can also inhibit the activity of FAAH and MAGL enzymes. By doing so, it increases the availability of endocannabinoids in the ECS, leading to extended effects and enhanced signaling.
Indirect Mechanisms
Additionally, CBD can interact with other receptors in the body, such as serotonin and vanilloid receptors, which are involved in pain modulation and mood regulation.
Potential Benefits of CBD and the ECS
Due to its influence on the ECS, CBD carries numerous potential benefits. However, it is important to note that research is still ongoing, and CBD should not be considered a cure-all. Here are some of the areas where CBD shows promise:
Pain Management
CBD may help alleviate chronic pain by interacting with the ECS and reducing inflammation. Studies have shown its effectiveness in relieving pain associated with conditions like arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and fibromyalgia.
Mood and Anxiety Regulation
CBD has shown anti-anxiety and antidepressant properties, which may be attributed to its ability to modulate neurotransmitter receptors like serotonin. It could potentially help manage conditions such as generalized anxiety disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Neuroprotection
Research suggests that CBD’s interaction with the ECS may have neuroprotective effects. It could potentially help in the treatment of neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy.
Conclusion
CBD’s interaction with the endocannabinoid system holds significant promise for various health conditions. While CBD-based products are widely available, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating CBD into your wellness routine. Understanding the intricacies of the endocannabinoid system provides valuable insights into how CBD can potentially work within our bodies, promoting balance and well-being.
